A solar panel mounting system (also called a solar racking system) is the structural framework that securely attaches solar panels to a surface (like a roof, ground, pole, or carport) and positions them at the optimal angle to capture sunlight.
It’s much more than just “holding panels up.” A good mounting system is critical for:
- Structural Integrity: Safely supporting the panels for decades, resisting wind uplift, snow loads, seismic activity, and other environmental stresses.
- Optimal Tilt and Orientation: Positioning panels at the best angle (tilt) and direction (azimuth, usually south in the Northern Hemisphere) to maximize sunlight exposure and energy production.
- Ventilation: Allowing airflow under the panels to prevent overheating (which reduces efficiency) and minimize moisture buildup.
- Protection: Safeguarding the roof or ground surface from damage and preventing water leaks (especially on roofs).
- Durability: Constructed from corrosion-resistant materials (like anodized aluminum, galvanized steel, stainless steel) to withstand harsh weather for 25+ years.
- Accessibility: Facilitating installation, maintenance, and potential future panel replacement.
- Aesthetics: Providing a clean, organized, and visually appealing installation.

Key Components of a Typical Mounting System:
- Mounts / Attachments: The points that physically connect the system to the structure.
- Roof: Roof attachments (like flashing brackets, standoffs, L-feet) that seal around roof penetrations or clamp onto seams (for standing seam metal roofs).
- Ground: Foundations (concrete footings, ground screws, ballasted blocks).
- Pole: Top-of-pole or side-of-pole mounts.
- Rails: Long, horizontal aluminum extrusions running parallel to the rows of panels. Panels attach to these rails.
- Clamps / Brackets: Hardware that secures the panels to the rails.
- Mid Clamps: Connect the middle edges of adjacent panels.
- End Clamps: Secure the outer edges of the first and last panels in a row.
- Flashing: Waterproof seals (integrated with roof mounts or separate) that prevent leaks around roof penetrations.
- Mid & End Clamps: Hardware that secures the panels to the rails (mid clamps between panels, end clamps on the ends of rows).
- Tilt Legs / Risers (Optional): Used on flat roofs to achieve the desired tilt angle.
- Ground Mount Components: Posts, beams, and pile drivers for securing the structure into the earth.
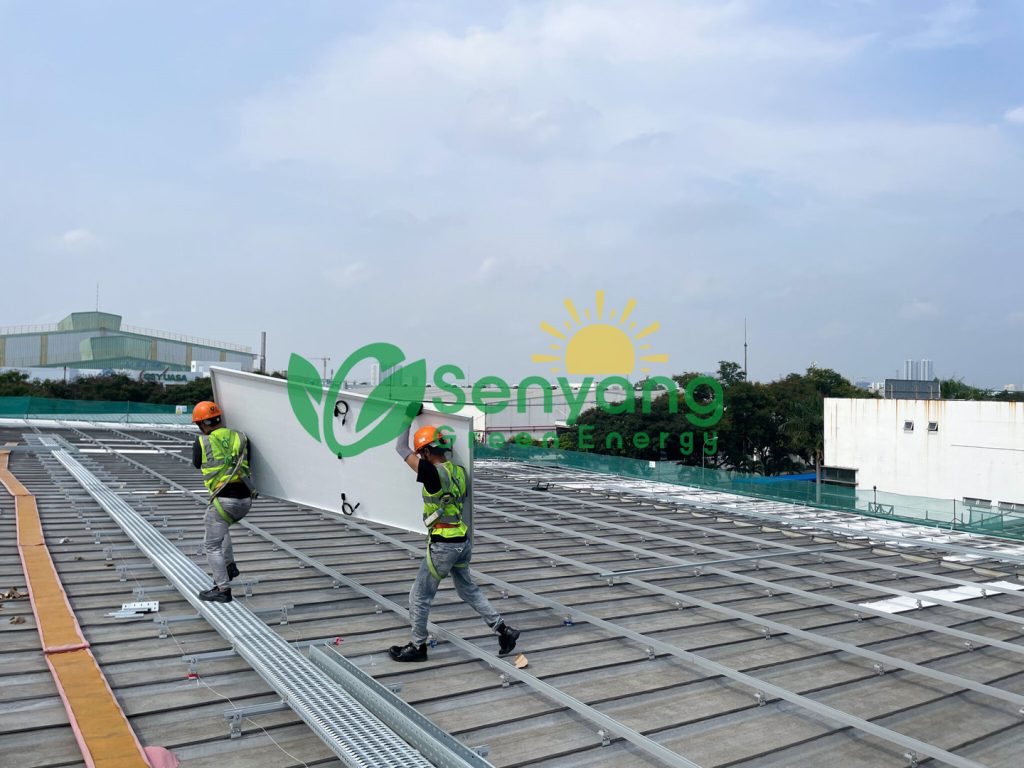

Main Types of Solar Mounting Systems:
- Roof Mounts:
- Pitched Roof Mounts: The most common type. Attached directly to rafters/trusses through the roofing material.
- Penetrating: Secured with bolts penetrating the roof deck, requiring flashing for waterproofing. Most secure.
- Ballasted: Uses weighted blocks (concrete, etc.) instead of roof penetrations. Common on large flat commercial roofs but heavy. Rare for homes.
- Standing Seam Clamps: Attach directly to the vertical seams of metal roofs without penetration.
- Flat Roof Mounts: Use tilt legs/risers to angle the panels and are either:
- Penetrating: Secured with anchors through the roof membrane.
- Ballasted: Held down by weights on the roof surface.
- Pitched Roof Mounts: The most common type. Attached directly to rafters/trusses through the roofing material.
- Ground Mounts: Installed on open land. Offer flexibility in orientation/tilt and easier access.
- Standard Fixed-Tilt: Panels set at a fixed optimal angle.
- Pole Mounts: Panels mounted on one or more poles, often allowing for:
- Fixed Tilt: Simple pole structure.
- Tracking Systems: Motored systems that tilt panels to follow the sun throughout the day (Single-axis or Dual-axis), significantly increasing energy yield but at higher cost and complexity.
- Specialty Mounts:
- Carport/Canopy Mounts: Integrate solar panels into parking shade structures or building awnings.
- BIPV (Building-Integrated Photovoltaics): Panels act as the actual roofing material or facade element.
- Floating Solar: Mounts designed for installation on bodies of water.

Why the Mounting System Matters:
- Safety: Prevents panels from detaching in extreme weather.
- Performance: Ensures panels are positioned correctly for maximum sunlight capture.
- Longevity: Protects your roof and ensures the system lasts as long as the panels.
- Warranty: Proper installation using certified systems is often required for panel and roof warranties.
- Efficiency: Proper airflow prevents efficiency loss due to heat.
- Cost: Racking typically accounts for a significant portion (10-20%) of the total system cost.
Choosing the right solar mounting system involves considering your roof type/condition, local climate (wind, snow), ground conditions, desired tilt/angle, budget, and aesthetics. We can suggest to Professional installers select and engineer the appropriate system for each specific project. Pls feel free contact to us.
